Introduction
As global industries shift toward sustainability, evaluating the environmental impact of manufacturing processes has become a priority. Among the most widely used methods — CNC machining, 3D printing (additive manufacturing), and injection molding — each has unique strengths and trade-offs in terms of material efficiency, energy consumption, waste generation, and lifecycle impact.
This article provides a comparative analysis to help engineers, product designers, and manufacturers select the most sustainable option based on production volume, material choice, and application requirements.
Environmental Factors in Manufacturing
Key factors influencing environmental impact include:
- Material Utilization – How efficiently raw materials are converted into final parts.
- Energy Consumption – The amount of energy required during production.
- Waste Generation – Scraps, supports, and rejected parts.
- Lifecycle Impact – Durability, recyclability, and potential for re-use.
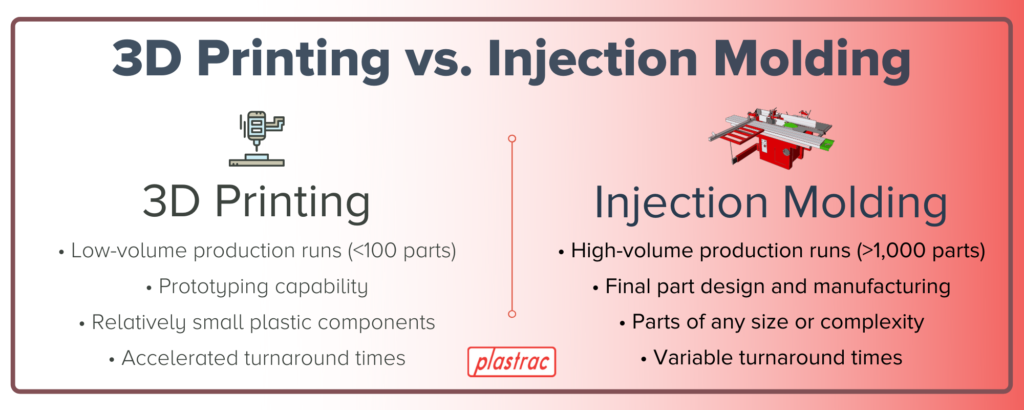
- Production Volume Efficiency – How sustainability changes between prototyping and mass production.
Comparison of CNC, 3D Printing, and Injection Molding
| Factor | CNC Machining | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Utilization | Subtractive process, high material waste (up to 60–70% scrap for complex parts). | Additive process, nearly zero material waste, but support structures add some waste. | High efficiency once molds are built, minimal waste per part. |
| Energy Consumption | High (continuous spindle, coolant, cutting tools). | Moderate to high (depends on technology: SLS/SLM are energy-intensive, FDM lower). | High upfront (mold-making), low per-part energy usage in mass production. |
| Waste Generation | Significant chips and coolant disposal required. | Limited waste; recycling possible but depends on polymer type. | Very low waste in production; defective parts are main contributors. |
| Lifecycle Impact | Long-lasting parts, but high carbon footprint per unit for small runs. | Potential for lightweight and complex designs; material recyclability is limited. | Durable, high-volume parts; mold reusability reduces long-term footprint. |
| Best Use Case (Sustainability) | Low to mid-volume, metals, high-precision parts. | Rapid prototyping, low-volume custom parts, design validation. | Large-scale production with repeatability and minimized per-unit footprint. |
Deeper Insights
- CNC Machining
- Strength: Works well for metals and high-precision requirements.
- Weakness: High material waste (scrap metals often recycled, but energy-intensive).
- 3D Printing
- Strength: Ideal for lightweight structures and complex geometries, reducing material usage.
- Weakness: Energy-intensive for certain technologies (laser-based systems).
- Injection Molding
- Strength: Most eco-efficient for high-volume runs due to low per-unit waste and energy.
- Weakness: High initial mold fabrication footprint, unsuitable for very small batches.
How to Improve Sustainability
- CNC Machining: Use near-net-shape blanks, recycle metal chips, optimize toolpaths.
- 3D Printing: Select recyclable polymers, use efficient support structures, adopt binder jetting for lower energy.
- Injection Molding: Optimize mold design, use bio-based polymers, implement closed-loop recycling of runners and defective parts.
Conclusion
There is no single “greenest” manufacturing process — the environmental impact depends on production scale, material, and application.
- For rapid prototyping and customization, 3D printing offers material efficiency advantages.
- For small to medium batches requiring high precision, CNC machining remains viable if recycling measures are in place.
- For large-scale production, injection molding is the most sustainable, with minimal waste and energy use per unit.
At Ze-tech Mold, we provide CNC machining, 3D printing, and injection molding services, helping clients balance sustainability, cost, and performance with tailored manufacturing solutions.
