Introduction
Silicone vacuum casting is one of the most cost-effective and flexible manufacturing methods for producing low-volume prototypes and functional parts. It’s widely used in industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices — especially when you need high-quality plastic-like parts without investing in expensive injection molds.
However, achieving consistent results requires more than just pouring resin into a silicone mold. Each step — from master model preparation to degassing and curing — demands careful control. In this article, we’ll explore the key points to pay attention to during the silicone vacuum casting process to ensure precision, quality, and efficiency.
Master Model Preparation
The vacuum casting process begins with a master model, typically created through CNC machining or 3D printing (SLA or SLS).
Tips:
- Ensure dimensional accuracy — imperfections on the master will replicate in every cast part.
- Choose a material that can withstand high mold-making temperatures (40–70°C).
- Apply a gloss or matte surface finish based on desired part aesthetics.
| Step | Consideration | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Master Model Design | Avoid sharp edges and undercuts | Easier demolding |
| Surface Finish | Polished or textured as required | Affects final appearance |
| Durability | Model should withstand multiple mold pourings | Ensures mold precision |
Silicone Mold Making
The quality of the silicone mold directly determines the fidelity and consistency of the cast parts.
Key Points:
- Use high-quality RTV silicone with the right hardness (usually 20–30 Shore A).
- Maintain proper temperature and curing time — fast curing can cause internal stress.
- Use vacuum degassing before pouring to remove trapped air bubbles.
Tip: Avoid reusing molds beyond their lifespan (typically 15–25 castings), as dimensional accuracy will degrade.
Mixing and Degassing the Resin
Resin choice and handling play a huge role in part quality. Common resins include polyurethane (PU), ABS-like, or transparent epoxy materials.
Best Practices:
- Mix resin components according to manufacturer’s ratio — inaccurate mixing leads to soft or brittle parts.
- Always degass under vacuum to remove microbubbles before pouring.
- Maintain temperature control (20–30°C) for consistent curing.
| Common Defects | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Air bubbles | Insufficient degassing | Extend vacuum time |
| Soft or sticky surface | Wrong mix ratio | Measure precisely |
| Warping | Uneven curing | Maintain stable temperature |
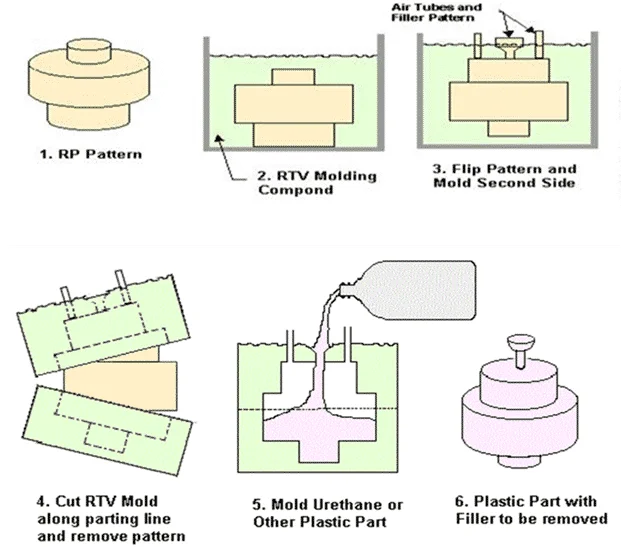
Casting and Curing
Once the resin is poured into the silicone mold under vacuum, curing begins.
Tips for Optimal Results:
- Keep the mold in a vacuum chamber to prevent air entrapment.
- Follow the recommended curing time and temperature (usually 60–80°C for 2–4 hours).
- For complex geometries, consider post-curing for enhanced mechanical strength and temperature resistance.
Demolding and Finishing
After curing, demolding should be done carefully to avoid damaging the silicone mold or the cast part.
Key Steps:
- Allow the part to cool down before demolding.
- Use release agents if necessary for fine-detail molds.
- Post-process parts with trimming, sanding, or painting for final appearance.
Quality Control and Reproducibility
Consistent quality in vacuum casting relies on process documentation and testing.
| Inspection Aspect | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Check | Calipers or 3D scanner | Verify tolerance |
| Surface Inspection | Visual or microscopy | Detect bubbles or cracks |
| Mechanical Testing | Tensile or flexural tests | Validate part performance |
Conclusion
Silicone vacuum casting remains a vital bridge between rapid prototyping and low-volume production. By paying close attention to material preparation, vacuum control, curing, and mold maintenance, manufacturers can achieve parts that closely mimic injection-molded components — at a fraction of the cost and lead time.
Mastering these details not only improves part quality but also enhances efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape.
